
Handwritten traditional signatures on actual papers require an in-person presence or mailing, slowing down procedures. Digital e-signatures save time, cut documentation, and enable rapid online signing. They also offer enhanced security features such as encryption and audit trails.
Signing papers has been an important part of business and legal dealings for hundreds of years. They prove who you are and that you agree to something. However, as digitalization has grown, electronic signatures (e-signatures) have become a popular choice instead of printed signatures.
But what’s the real difference between them? Which is safer, more legally binding, or easier to use? This blog post will discuss the main ways that standard and electronic signatures are different, as well as their pros, cons, and future trends.
- Growth: E-signature usage exploded from 198M to 4.75B transactions in 5 years, projected to hit $18.4B by 2026.
- Costs: U.S. businesses waste $8B/year on paper. E-signatures cut document costs by 85% and shipping by 80%.
- Workflow: 65% of companies lose a day waiting for physical signatures. Paperless firms reduce errors by 90% and eliminate printing/copying hassles.
What is a Traditional Signature?
A traditional signature is a handwritten name or unique mark made on a physical document to confirm a person’s assent and identify them. Used for centuries, it is still a legally approved approach for verifying official papers, contracts, and agreements. Every person’s signature serves as a personal identification tool that guarantees responsibility and confirms their intention to support the requirements of the agreement.
Characteristics of Traditional Signatures:
- Produced with pen and paper.
- physically kept, organized, and filed
- Calls for either in-person signing or mailing.
- distinctive to every person
Common Uses:
- Legal contracts
- Bank documents
- Government forms
- Real estate agreements
What is an E-Signature?
An e-signature (electronic signature) is a secure, digital method to sign documents electronically, replacing the need for handwritten signatures. It can include a typed name, a scanned image of a handwritten signature, or a cryptographic-based digital signature. E-signatures are legally binding and use encryption to verify the signer’s identity, ensure document integrity, and validate intent to approve agreements, contracts, or forms. They streamline workflows by enabling quick, remote signing and sharing of digital documents.
Types of E-Signatures:
- Simple E-Signature: scanned or typewritten name or signature.
- Advanced E-Signature makes use of email verification or OTP as a means of authentication.
- The digital signature is encrypted and complies with legal standards such as eIDAS, UETA, and the ESIGN Act.
Common Uses:
- Online contracts
- HR onboarding
- Loan approvals
- Business agreements
Key Differences Between Traditional and E-Signatures
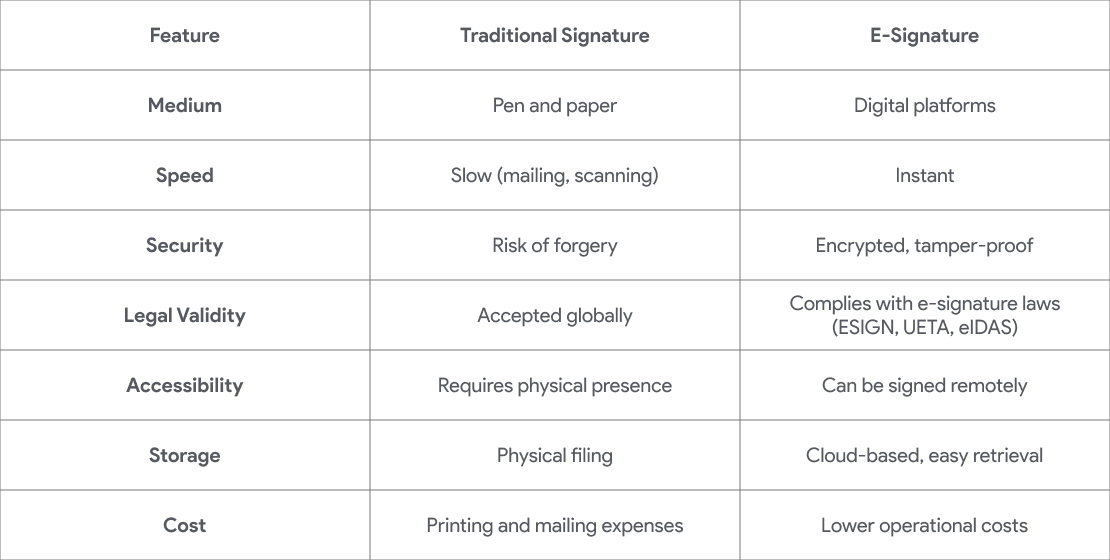
Advantages of Traditional Signatures
- Widely Recognized – accepted everywhere without the need for technology.
- Personal Touch – Offers a tangible, human element that feels more authentic in certain situations.
- No Tech Barriers – Requires no digital tools, devices, or internet access.
Advantages of E-Signatures
- Faster Processing—Sign and send documents in seconds.
- Enhanced Security—Digital audit trails and encryption reduce fraud.
- Cost-Effective—Saves money on printing, shipping, and storage.
- Eco-Friendly—Reduces paper waste.
- Remote Accessibility—Sign in from anywhere, anytime.
Challenges and Limitations
Traditional Signatures:
- Slow process: Hands-on handling and mailing are required.
- Risk of Loss or Theft: Paper papers can get lost or faked.
- Problems with storage: Paper files take up room.
E-Signatures:
- Tech Dependency – Requires internet and digital literacy.
- Legal Concerns – Some countries have strict e-signature laws.
- Security Risks – If not properly encrypted, it can be vulnerable to hacking.
When to Use Traditional vs E-Signature?
Use Traditional Signatures When:
- The law requires wet signatures (e.g., certain wills, court documents).
- The signer is not comfortable with digital tools.
- A physical copy is needed for archival purposes.
Use E-Signatures When:
- Speed and efficiency are crucial (e.g., business contracts).
- Remote signing is necessary (e.g., international agreements).
- You want to reduce paperwork and costs.
Future of Signatures in the Digital Age
E-signatures are evolving as governments and companies embrace digital transformation. Trends influencing the future consist of:
- Blockchain-based signatures for enhanced security.
- Biometric signatures (fingerprint, facial recognition).
- AI-powered verification to detect fraud.
- Global standardization of e-signature laws.
Although their use may fade in favor of speedier, safer digital alternatives, traditional signatures won’t vanish totally.
FAQs: Traditional Signature vs E-Signature
- Are e-signatures legally valid?
Yes, e-signatures are legally binding in most countries, including the U.S. (under the ESIGN Act) and the EU (under eIDAS regulations). However, certain documents, like wills or court orders, may still require traditional signatures. - Can e-signatures be forged or tampered with?
Advanced e-signatures (like digital signatures) use encryption and audit trails to prevent tampering. Basic e-signatures (e.g., scanned handwritten signatures) can be forged if not secured properly. Always use trusted e-signature platforms for critical documents. - When am I required to use a traditional signature?
Traditional “wet” signatures are mandatory for specific legal documents, such as wills, adoption papers, or court filings in some jurisdictions. Always check local laws or consult a legal expert for clarity. - Do all countries accept e-signatures?
Most countries recognize e-signatures, but regulations vary. For example, India requires Aadhaar-based authentication for some documents, while others may need additional verification. Research local laws for international agreements. - How do e-signatures work?
E-signatures are created using digital tools.
- Upload a document to an e-signature platform.
- The signer adds their signature (typed, drawn, or uploaded).
- The platform encrypts the document and records details like timestamps and IP addresses.
- Both parties receive a signed copy via email or cloud storage.
Conclusion
Today’s commercial and legal landscapes embrace both traditional and electronic signatures, each serving distinct needs. E-signatures deliver unmatched speed, security, and efficiency, while traditional signatures offer a sense of familiarity. The choice between them depends on legal requirements, user preference, and security considerations. Yet, as technology advances, e-signatures continue to dominate as the preferred method for global business—streamlining transactions and accelerating deals worldwide.
Ready to experience seamless, secure, and legally compliant e-signatures? Explore SignPe.com today and transform the way you sign!